#coding and warfarin management
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
feeling angry - at what? damn preceptors and humans that won’t respond to text messages.
0 notes
Text
OPRA Exam Success: Key Strategies for Effective Prep

Introduction
The Overseas Pharmacist Readiness Assessment (OPRA) is a crucial milestone for international pharmacists seeking registration in Australia. With the exam set for March 3, 2025, now is the time to refine your study strategies. At Elite Expertise, we recognize the challenges of this competitive exam and have compiled expert-backed tips to help you maximize your preparation.
1. Understand the OPRA Exam Syllabus
A clear understanding of the syllabus is essential for focused preparation.
Review the official OPRA exam guidelines.
Identify key areas: clinical pharmacy, pharmacy practice, biomedical sciences, and pharmaceutical sciences.
Allocate study time based on topic weightage.
2. Develop a Structured Study Plan
A well-organized schedule ensures effective revision and retention.
Prioritize high-weightage subjects.
Dedicate time for daily self-tests and problem-solving.
Conduct weekly revisions to reinforce concepts.
3. Practice Pharmacy Calculations
Pharmaceutical calculations are a major component of the exam.
Solve pharmacokinetics, dosage, and dilution problems.
Use past exam papers and online question banks.
Review mistakes to improve accuracy.
4. Utilize Flashcards for Quick Revision
Flashcards enhance memory retention for key formulas.
List essential calculation formulas.
Review them daily.
Use color-coded flashcards for different calculation types.
5. Memorize Drug Classifications with Mnemonics
Mnemonics simplify pharmacology concepts and improve recall.
Create personalized mnemonics for drug classifications.
Use visual aids for enhanced retention.
6. Use Flowcharts for Mechanisms of Action (MOA)
Understanding drug mechanisms is critical for OPRA success.
Create flowcharts to simplify complex pharmacological processes.
Focus on high-yield MOA topics like anticoagulants, antihypertensives, and antibiotics.
7. Organize Drug Interaction and Antidote Charts
Recognizing drug interactions and toxicity management is vital.
Chart significant interactions (e.g., Warfarin + NSAIDs → Increased bleeding risk).
Create a separate antidote reference for common toxicities.
8. Enhance Visual Memory with Study Notes
Visual aids support long-term retention.
Place key notes, flowcharts, and mnemonics in your study area.
Keep notes concise and focused on crucial topics like dose conversions and ADRs.
9. Strengthen Clinical Knowledge with Case Studies
Case-based learning sharpens problem-solving skills.
Practice case studies covering symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment.
Develop critical thinking and decision-making skills.
10. Memorize Key Biomedical Science Values
Biomedical sciences frequently appear in OPRA exam questions.
Use flashcards for lab values and therapeutic ranges.
Review them daily for better recall.
11. Avoid Unnecessary Study Materials
Quality over quantity is key when selecting resources.
Rely on reputable textbooks and official exam references.
Join study groups to access valuable insights from successful candidates.
12. Use Audio Learning for Reinforcement
Listening to recorded notes can enhance retention.
Record key concepts like MOAs, ADRs, and drug classifications.
Listen during breaks, commutes, or workouts.
13. Compare Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
Comparison charts help clarify complex concepts.
Create side-by-side comparisons of key topics:
First-order vs. Zero-order kinetics
Competitive vs. Non-competitive inhibition
Conclusion
Ace the OPRA Exam with Smart Preparation!
Success in the OPRA exam requires strategic planning, dedicated practice, and effective revision techniques. At Elite Expertise, our experienced clinical pharmacists, Mr. Arief Mohammad and Mrs. Harika Bheemavarapu, provide expert guidance for international pharmacy exams like OPRA.
With the right approach and expert-led coaching, you can boost your confidence and maximize your chances of passing the OPRA exam on March 3.
0 notes
Text
The Evolution of the CPT Code for INR Check in Modern Healthcare
In the complex and ever-changing world of healthcare, precision and efficiency are key to successful medical billing and patient care. One critical aspect of this process is the Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) system. Among its many codes, the CPT code for INR check plays a vital role in documenting and billing for essential diagnostic tests. This blog examines the evolution of the CPT code for INR check, from its early beginnings to its pivotal role in modern healthcare systems.
What is the CPT Code for INR Check?
The CPT code for INR check is a unique identifier used in medical billing to document and charge for International Normalized Ratio (INR) testing. INR tests are essential for patients on anticoagulant medications like warfarin, as they measure the blood’s ability to clot. Accurate use of this code ensures healthcare providers receive proper reimbursement while maintaining a standardized approach to patient care and billing practices.
The Early Stages: Manual Systems and General Codes
In the past, medical billing relied heavily on manual processes, which were prone to errors and inefficiencies. INR tests were often recorded under general laboratory codes, making it challenging to differentiate and manage specific diagnostic procedures. This lack of specificity led to billing inaccuracies and inefficiencies in patient care documentation.
The introduction of the CPT coding system in the 1960s began to address these challenges. Though INR testing did not have a dedicated code initially, the system’s development laid the foundation for creating specialized codes to streamline billing and reporting.
Advancing Specificity: Dedicated CPT Code for INR Check
As anticoagulant therapies became more widespread, the need for accurate billing codes grew. The establishment of a specific CPT code for INR check marked a turning point in medical documentation and billing. This development provided:
Clarity in Billing: Assigning a unique code to INR checks reduced confusion and improved claims processing.
Improved Data Management: Accurate coding made it easier to track INR tests and assess patient outcomes.
Compliance with Regulations: Specific codes supported adherence to healthcare standards and facilitated reporting for quality assurance programs.
The Digital Revolution: How Technology Transformed the CPT Code for INR Check
With advancements in technology, the application of the CPT code for INR check has become more efficient and accurate. Electronic Health Records (EHR) and automated billing systems have seamlessly integrated these codes into healthcare workflows, resulting in:
Reduced Errors: Automated systems minimize human error in coding and claims submissions.
Streamlined Workflows: Digital platforms simplify the documentation process, allowing providers to focus on patient care.
Enhanced Patient Outcomes: Real-time data from INR tests enables healthcare professionals to adjust treatment plans promptly.
Emerging Trends and the Future of CPT Code for INR Check
As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, so too does the application of the CPT code for INR check. Key trends shaping its future include:
Telemedicine Integration: With the rise of remote healthcare, INR testing at home is becoming more prevalent. The CPT code for INR check facilitates billing for telehealth services, making care more accessible.
AI and Automation: Artificial intelligence in billing systems promises even greater accuracy and efficiency in processing CPT codes.
Regular Updates: The CPT coding system undergoes periodic revisions to reflect advancements in medical practices, ensuring it remains relevant and effective.
The journey of the CPT code for INR check demonstrates its indispensable role in modern healthcare. From its origins as a general laboratory code to its current integration with advanced technologies, this code has revolutionized medical billing and patient care. As technology continues to advance, the CPT code for INR check will remain central to streamlined healthcare operations.
At PatientSelfTesting, we are committed to helping patients and providers navigate the complexities of modern healthcare. Staying informed about the CPT code for INR check ensures better care and smoother operations. Trust PatientSelfTesting to keep you updated and supported as healthcare continues to evolve.
0 notes
Text
What & Hows of Pharmaceutical Waste Disposal in Daytona Beach and Orlando, FL
Getting rid of the waste generated inside a home is easy enough. The waste may be stored in a garbage bag and disposed of according to the community's rules. The same does not apply to research labs, healthcare, or pharmacies, which usually accumulate vast quantities of medicines and other related waste. Management needs to be well aware of safety measures and make efforts to comply with the standard procedures for pharmaceutical waste disposal in Daytona Beach and Orlando, FL. First and foremost, the staff at such facilities must be informed about the type of waste generated by the minute. Segregating the biohazards and pharmaceutical waste into a color-coded container, as OSHA recommended, is also vital. There are several types of pharmaceutical waste. It is advisable to identify them and store them as per the regulations. Some of the items that may be regarded as pharmaceutical waste include the following:-
Solid Pharmaceutical Waste · Sharps such as used scalpels, needles, and/or syringes · Contaminated masks, gloves, bandages, as well as IV bags and tubing · Drugs that contain hazardous / non-hazardous chemicals · Empty pill bottles, liquid medicine containers, blister packs, and/or ointment tubes · Medicine distribution devices like inhalers, auto-injectors, and nebulizers
Liquid Pharmaceutical Waste Liquid waste accumulates within the facilities or laboratories during processing or other operations. Sludge from chemical processing and contaminated solvents used for cleaning the containers and tanks are also regarded as pharmaceutical waste.
The unused drugs, both solid and liquid, may be mailed to the seller/dealer instead of being retained within the facility.
The process of disposal of pharmaceutical waste must be done as follows:
· Segregation of pharmaceutical waste from biohazardous waste. The latter is considered most dangerous for health and needs to be disposed of separately
· Removal of all controlled substances such as opiates and benzodiazepines. These substances need to be handled according to the U.S. Drug Enforcement Agency regulations
· Removal of trace chemotherapy waste. Medicinal drugs and other substances used during Chemotherapy can be deadly for a healthy human being, even when exposed to a minuscule amount. Trace chemotherapy waste usually includes
l Empty medication vials
l IV tubing used to deliver medication l Medical gloves worn by staff during Chemotherapy · Removal of hazardous waste. The Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) categorizes certain chemicals as hazardous and extremely risky for the general public. Drugs such as warfarin, lindane, and mitomycin are considered to be hazardous waste and must be disposed of separately
Packaging of the remaining waste to be stored in OSHA and/or FDA-recommended blue color-coded containers fitted with tight white lids
Proper biomedical waste disposal in Orlando and Kissimmee, FL, is also essential to ensure the sanitation and safekeeping of the facility's patients, staff, and visitors.
It is best to contact a service provider that excels in transportation, treatment, and proper waste disposal. Once the storage containers are handed over, such companies are sure to maintain compliance with regulatory standards.
#pharmaceutical waste disposal in Daytona Beach and Orlando#FL#biomedical waste disposal in Orlando and Kissimmee
0 notes
Text
Lupine Publishers | Caregiver’s Oral Healthcare Practices And The Level of Utilisation Of Oral Health Services and The Dental Caries Experience Of 3-12-Year-Olds Suffering From Heart Disease in Nairobi, Kenya
Lupine Publishers | Dental and Oral Health Journals
Abstract
Cardiac diseases require that there is the meticulous maintenance of oral hygiene to avoid bacteremia, which has been associated with rheumatic heart disease and bacterial endocarditis. The aim was to establish the utilisation of oral health care and oral health practices of the caregiver about the oral hygiene and caries experience of children aged 3-12 years suffering from heart disease and were attending three pediatric cardiology clinics in Nairobi, Kenya. The study was descriptive and cross-sectional. It involved a study sample of children suffering from different types of cardiac conditions and attending the Pediatric cardiac clinics in three public institutions in Nairobi Kenya. The instruments the caregivers used to brush the children’s teeth were the toothbrush 61(75%); chewing stick 14(17%) and 6 (8%) never cleaned their teeth. Children who used a chewing stick had a lower dmft of 1.40±2.98 compared to a dmft of 3.22±3.59 among children who used the toothbrush, with Mann Whitney U, Z p=0.024 (p≤0.05).The children who brushed their teeth had a lower mean plaque score of 1.68±0.58 compared those who did not clean with a mean plaque of 2.28±0.40 with a Mann Whitney U, Z=-2.611, p=0.009(p≤0.05). It was noted that the children who had visited a dentist had a higher caries experience with a dmft of 4.18±4.13 and DMFT of 1.16±1.92. However, the children who had never sought treatment at a dental facility had lower dmft of 1.89±2.88; and DMFT of 0.36±1, and the differences were statistically significant with Mann Whitney U, Z p=0.008(p≤0.05). The plaque scores and caries experience were high in children whose caregivers had low aggregate utilisation of the oral health care facilities. However, those who had a low aggregate of oral hygiene practices had slightly higher plaque scores and caries experience.
Keywords: Cardiac Disease; Children; Utilisation; Oral Health Services; Caregivers
Introduction
Populations with chronic medical illness or other disabilities had the most unmet needs for oral health services [1], with poor oral hygiene and increased caries experience than the general population. For a child from a low-income family with heart disease, this means an added economic burden in an already tricky situation [2], as heart diseases necessitate regular dental check-ups and maintenance of meticulous oral hygiene. This concern has even been highlighted with new proposals on changes in the guidelines relating to prophylaxis against infective endocarditis [3,4]. The oral conditions may have a considerable impact on the general health status and quality of life of otherwise healthy children, but their effects on those children with acute and chronic illness can be more dangerous [5]. Children with cardiac defects and diseases are at increased risk or even life-threatening complications [6]. Hence the need for preventive dental health care geared to reducing the risks associated with management of the oral conditions under general anaesthesia. Also, the prolonged bleeding from warfarin medication often taken By the children [7-10]. Poor oral hygiene may give rise to a frequent bacteraemia under normal physiological conditions, and this can lead to a permanent risk of developing heart disease [11-14]. Two common oral diseases, namely periodontal and dental caries, though preventable, are still more prevalent in Kenya [15,16]. The children with heart disease have the disadvantage that their caregivers are preoccupied with the with the primary medical condition the cardiac disease, resulting in the neglect of other facets of the child’s total health [17]. The Kenya National Oral Health policy document has already indicated that the dmft value for Kenyan 5-year old children as at 2002 was 1.5±2.2, while 43% of 6-8-year-old children had caries [15], underscoring the fact that caries is still very rampant amongst the child population in Kenya.
The study was descriptive and cross-sectional where all the patients aged 3 to 12 years and their caregivers attending paediatric cardiology clinics over a three month period at Kenyatta National Hospital (KNH), Gertrude’s Garden Children’s Hospital (GGCH) and Mater Hospital. A Purposive sampling had been used to select the study hospitals. Based on Kliegman. study, the study population sample was determined as 79 cases. However, 81 patients were recruited in the study. A semi-structured questionnaire was used to collect information on the socio-demographic characteristics of the children and the parent/guardian habits on oral health practices and utilization of oral health services. As children waited to consult the cardiologist clinical examinations done to record the oral health status. The examination was conducted using sterilized instruments and under natural daylight, with the participants seated on a chair facing the window. Great care was taken during periodontal probing for gingivitis, to avoid initiating bleeding that could lead to septicaemia as the children were not on prophylactic antibiotics. The results were recorded on predesigned individual questionnaire sheets, and a record of dental caries and plaque was done. The dental caries was then recorded as dmft for the primary dentition and DMFT in the permanent [18,19], and the dental plaque was marked based on the Loe and Silness plaque score index [20]. Before commencement of the study, the examiner was calibrated by an experienced paediatric dentist on the collection of data relating to dental caries, and dental plaque Cohen’s kappa index score of 0.87 and 0.85 (n=10) was obtained for dental caries and plaque score respectively. The questionnaire was pre-tested before use. A duplicate clinical examination was also performed by the examiner to determine intra-examiner consistency, with results of Cohen’s kappa index score of 0.91 and 0.86 (n=12) being obtained for dental caries and plaque score respectively.
Data analysis
The data collected was cleaned, coded and analyzed using SPSS version 17-computer software from SPSS Inc. IL. The results obtained were compared and tested using Kruskal Wallis Chi-square and Mann Whitney U statistical tests, with statistical significance pegged at 95% confidence interval.
Results
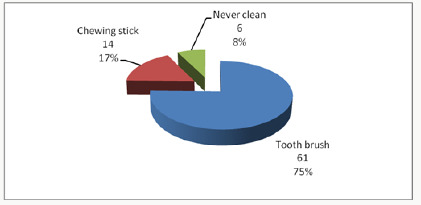
The 81 children in the study, 44 (54.3%) were males and 37 (45.7%) females. Their ages ranged between 3-12 years with a mean age of 8.16 years (± 2.81 SD), and the 6-9-year-olds accounted for the most substantial proportion of 33 (40.7%) compared to the 3-5 year-olds who formed 16(19.8%). The differences in ages and gender were not statistically significant Chi χ2 =1.287, two df, p=0.525(p≤0.05). A total of 37(46%) children were from rural areas, 28(34%) were from Nairobi, and 16(20%) were from other urban centres other than Nairobi. The distribution of the children according to the type of heart disease, rheumatic (RHD) accounted for 36(44.5%) while infective endocarditis (IE) affected 4(4.9%). The duration since diagnosis of the cardiopathy ranged from less than one year to 12 years. Nearly half of the children, 40 (49%) had been diagnosed with the disease for a duration of between 1 to 5 years, while those who had been diagnosed more than five years and those less than one year accounted for 30% and 21% respectively. The caregivers’ oral health care practices that included how the child’s teeth were brushed; the frequency of brushing; and whether tooth brushing was supervised showed that 75(93%) children cleaned their teeth and 6(7%) children did not clean their teeth. Of the group that cleaned their teeth, 33(44%) did it twice a day, 29(39%) once a day while 16% once in a while/occasionally. About supervision, 62 (83%) reported cleaning their teeth without supervision while 13 were assisted by the caregivers. Inquiry on the ways the child’s teeth were cleaned, 75% (61) of the children used toothbrush and the rest of the results were as shown in Figure 1. The children who used toothpaste were 59 (79%) while 16 (21%) never use any toothpaste.
Figure 1:
Considering the utilisation of oral health care services by children with heart diseases; fifty-nine (72.8%), children had never visited a dentist or utilised oral health services. Among the 22 (27.2%) children who had been to a dentist, the dental procedure during the last appointment included extraction 10 (12.3%). Also cleaning/prophylaxis (1(1.2%)), consultation ; check-up 9(11.1%) and fillings 2(2.5%).Caregiver’s oral healthcare practices and the dental caries experience about the children five children who never cleaned their teeth had a higher dmft of 2.93±2.50 compared to a lower dmft of 2.89 ±3.54 among the 56 children who cleaned their teeth, and the differences were insignificant with p=0.957(p≤0.05).
The differences in the frequency of tooth cleaning, the eleven children who cleaned their teeth once in a while had a higher dmft of 3.36±5.29 and the 23 children who cleaned twice a day had lower dmft of 2.68±2.77, but.difference was not statistically significant with p=0.936(p≤0.05). The children who used a chewing stick had a lower dmft of 1.40±2.98 compared to a dmft of 3.22±3.59 among the 46 children who used the toothbrush, with the difference was not statistically significant, p=0.024(p≤0.05). The children who had visited the dentist apparently had a higher caries experience with dmft of 4.18±4.13 and DMFT of 1.16±1.92 when related to the children who had never visited a dentist, who had lower dmft of 1.89±2.88; and DMFT of 0.36±1. These differences in the results were statistically significant, p=0.008(p≤0.05). The rest of the results are as shown in Table 1. When the caregivers were classified into two groups based on the responses to the oral healthcare practices as being favourable or unfavourable practices,53 (86%) caregivers fell in the unfavourable oral healthcare practices. Fiftythree children whose caregivers displayed unfavourable practices had a higher dmft of 3.62±3.54 compared to dmft of 2.74±2.85 among the eight children whose caregivers displayed favourable oral healthcare practices. The difference was statistically significant with Mann Whitney U, Z= -1.297, p=0.197(p≤0.05). The mean plaque score was significantly lower among the 75 children who reported to cleaning their teeth with mean plaque scores of 1.68±0.58, compared to a higher mean PS of 2.28±0.40 among the six children who never cleaned their teeth with p=0.009(p≤0.05). Those children who used the toothbrush had lower mean plaque scores of 1.64±0.61. The children who cleaned more than twice a day had the lowest mean plaque score of 1.55±0.63; and those who cleaned their teeth occasionally had the highest mean plaque scores of 1.99±0.41, though these differences were not statistically significant with χ2 =0.067, 1df, p =0.936 (p≤0.05), Table 2. The mean plaque scores among the 22 (27%) children who had been to a dentist was mean PS of 1.68±0.55 compared to higher plaque score of 1.83±0.61 among the 59 (73%) children who had never been to a dentist Table 2. However, the difference was not significant, with p=0.422 (p≤0.05)
Table 1:
Table 2:
Discussion
Despite the majority of the respondents, 75(93%), with the majority reporting that their children cleaned their teeth, only 33(44%) of these children cleaned their teeth at least twice a day, 62(83%), of them, cleaning their teeth without supervision by the caregivers. Seven children had never visited a dentist to have teeth cleaned teeth cleaned. Also, some children had occasional cleaning of their teeth, and this puts the children the risk of developing early childhood caries, gingivitis, and poor oral health. The poor oral health may which may give rise to frequent transient bacteremia during mastication or tooth brushing. Other studies among children with heart diseases have reported that 55 % of the children brushed their teeth twice a day [21,22] and that 46.1% of the children brushed three times a day. Owino et al [26] reported that 67.5% of the 12-year-old children in a peri-urban area brushed their teeth. Franco et, al [25] in their study considered as disappointing the percentage of children with congenital heart disease who had never visited a dentist, a reflection of other results obtained in studies by Silva et al [23], Saunders et al.[18], and Fonseca et al [5]. In this study, the very high percentage of the children examined had never seen a dentist, with only 22(27.2%) of the children have been to a dentist before the stu dy. Moreover, even though, most of the treatment, which had been offered during their visit to the dentist, was extraction, just as reported in a study, Ober et al [24]. The finding is alarming since the American Heart Association recommends that children with heart disease should visit a dentist for the institution of preventive measures.
The lower frequency of dental visits in this study compared to other studies in developed countries could be because of the reasons that include the fact that; most of the caregivers are ignorant on the importance of preventive dental care among the children with heart disease. Most of the patients examined were of lower socioeconomic status, therefore, could not afford the treatment. Also; the dental facilities in Kenya are limited, inaccessible and most of them lack skilled dental personnel who are well trained to offer treatment to children with special needs. The use of other tooth cleaning devices like the chewing stick was illustrated in this study. Majority of the children who were using this device were mostly from rural areas where other tooth cleaning aids may not be available. The outstanding fact was that the children examined were from different residential backgrounds. The patients who used the chewing stick in this study had significantly lower dental caries experience than those who used the toothbrush. The low caries experience in the children who used the chewing stick may be because they could not afford the snacks between meals. The low could probably be explained by the fact most of the children who used the chewing stick were from rural areas where the dental caries experience was shown to be lower compared to urban centres possibly because of the difference in the diet. Also, some studies have demonstrated the cariostatic and bacteriostatic properties of some specific species of trees, which are used as chewing sticks. It is also possible that a few children who started to use the brush late in life after severe early childhood caries had been established could have skewed the high caries experience illustrated among the children who were using the brush.
The caregivers’ aggregate oral healthcare practices did not significantly influence the dental caries experience among the children in the present study. The lack of differences in the gadgets for cleaning the teeth may be due to the small sample size where there was a loss of statistical power. Fifty-three (65; 4%) children whose caregivers were classified as portraying “unfavorable practices” had higher caries experience with mean dmft of 3.62±3.54 (n=53) compared to 2.74±2.85 (n=8) among the children whose caregivers reported “unfavorable practices” on oral care. The children who had been to a dentist had a higher dmft than those children who had never been to a dentist. This finding illustrates that children visit a dentist when dental disease dental caries has already occurred and that the majority of the treatment offered was curative to relieve the symptoms, with little or no emphasis on preventive oral care. The lack of focus on preventive oral care was further illustrated by the high proportion of active, untreated caries component of dmft compared to filled or extracted teeth. Despite the fact that caregivers’ aggregate oral health care practices had no significant relationship with the oral hygiene of the children as noted earlier, thirteen children whose caregivers reported “favourable practices” had lower plaque scores of 1.69 ±0.54. However, the plaque scores of sixty-eight children whose caregiver’s had reported favourable practices had a mean plaque score of 1.73±0.59 slightly higher.The children who cleaned their teeth had significantly lower plaque scores compared to those children who never cleaned teeth. The children whose teeth were never cleaned were at high risk of developing sub acute bacterial endocarditis when compared to the children who cleaned teeth regularly. As during the tooth brushing process, there is the mechanical removal plaque thus reducing the possibility of increased bacterial colonization of the plaque and reducing chances of bacteraemia during mastication. It was noted the that toothbrushes were more effective in control of plaque compared to the use of chewing sticks, though there was no significant difference between the two groups. The results of these study showed that children who had been to a dentist displayed better oral hygiene than those children who had never been to a dentist, though there was no statistical difference. The difference perhaps indicates that the dentist visited previously could have offered oral hygiene instructions on good tooth brushing techniques. In addition to that, the caregivers’ aggregate oral healthcare practices did not significantly influence dental caries experience among the children. Those children whose caregivers were classified as portraying “unfavorable practices “on oral care, had higher caries experience with mean dmft of 3.62±3.54 (n=53) compared to 2.74±2.85 (n=8).
The children who had been to a dentist had higher dmft than those children who had never been to a dentist. The finding may be rationalised that children who visited the dentist they did so when dental caries had already occurred. The primary treatment offered was curative to relieve the symptoms, with little or no emphasis on preventive oral care. The situation was further illustrated by the high proportion of active, untreated caries component of dmft compared to filled or extracted teeth.
Conclusion
The utilization of oral health care and oral health practices of the caregiver of the children was low, and only apparent used in case of emergency mainly. The oral hygiene, gingival index and dental caries experience in the study population was high.
Study limitations
The study was only for three months. Hence children who had had appointments in the previous clinics were excluded. The small sample size based in three cardiology clinics may have created a bias. The clinic was limited to 3-23-year-olds excluding the older children 13-17 this is the policy on how paediatric age cut off as defined by the ministry of health.
Acknowledgment
We thank Professor Loice Gathece for contribution in the design of the study. The Kenyatta National Hospital and the University of Nairobi Ethics and Research Committee fors approval of the proposal. Alice Lakati who helped in statistical work and Dr. E. Kagereki and Dr. Kiprop for data entry. The Nurses and the staff at the Paediatric Cardiac clinics at the KNH, Mater Hospital and the Gertrudes’ Garden children Hospital for facilitating data collection during the clinical examinations for the patients. We acknowledge all the parents and children who participated in the study without whom the study would not have been a success.
For more Lupine Publishers Open Access Journal Click Here: https://lupinepublishers.us/ For more Dentistry Journal Articles please click here: https://lupinepublishers.com/dental-and-oral-health-journal/index.php To know more about open access publishers please click on Lupine Publishers.
Follow on Linkedin : https://www.linkedin.com/company/lupinepublishers Follow on Twitter : https://twitter.com/lupine_online
0 notes
Text
Hemostasis Tests (In Vitro Diagnostics) - Global Market Analysis and Forecast Model (COVID-19 market impact) published on
https://www.sandlerresearch.org/hemostasis-tests-in-vitro-diagnostics-global-market-analysis-and-forecast-model-covid-19-market-impact.html
Hemostasis Tests (In Vitro Diagnostics) - Global Market Analysis and Forecast Model (COVID-19 market impact)
Hemostasis Tests (In Vitro Diagnostics) – Global Market Analysis and Forecast Model (COVID-19 market impact)
Summary
Hemostasis Tests (In Vitro Diagnostics) – Global Market Analysis and Forecast Model (COVID-19 market impact) is built to visualize quantitative market trends within In Vitro Diagnostics therapeutic area.
The model discusses in detail the impact of COVID-19 on Hemostasis tests market for the year 2020 and beyond. Prothrombin (PT) and Activated Prothrombin (aPTT) tests represent the most widely used Hemostasis tests. These devices are frequently utilized for coagulation testing prior to surgery.
Specifically sources indicate that preoperative coagulation testing occurs in approximately 39%-55% of cases and in many instances is considered to be un-indicated and performed when bleeding history is negative. PT tests are also frequently used for monitoring of patients taking vitamin K antagonists such as warfarin, phenprocoumon, and acenocoumarol.
Each of the covered 39 country’s color-coded and fully-sourced market models are equipped with epidemiology based indications with procedure volumes. To increase the data transparency, the interactive excel deliverable covers installed base, new sales volumes, product usage, average selling prices, market size and company share/rank analysis (wherever available). Moreover, analyst comments with qualitative insight offer context for quantitative data.
Key Inclusions of the market model are –
Currently marketed Hemostasis tests and evolving competitive landscape – – Insightful review of the key industry trends. – Annualized total Hemostasis tests market revenue by segment and market outlooks from 2015-2030. – Granular data on total procedures, units, average selling prices and market values by segment.
Global, Regional and Country level market specific insights – – Qualitative market specific information is available with global trends further broken down into regional trends. In addition GlobalData analysts provide unique country specific insights on the market. – SWOT analysis for Hemostasis tests market. – Competitive dynamics insights and trends provided for Hemostasis tests market.
Drive the understanding of the market by getting the veritable big picture including an overview of the healthcare system. In addition the Market Access segment allows you to delve deeper into market dynamics with information on reimbursement policies and the regulatory landscape. – Country specific overview of the healthcare system. – Country specific reimbursement policies. – Country specific medtech regulatory landscape.
Robust methodologies and sources enable the model to provide extensive and accurate overview of the market. Demand and supply-side primary sources are integrated within the syndicated models, including Key Opinion Leaders. In addition, real world data sources are leveraged to determine market trends; these include government procedure databases, hospital purchasing databases, and proprietary online databases.
Companies covered: Abbott laboratories, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Siemens Healthineers AG, Diagnostica Stago SAS, Werfen Life Group SAU and Others
Countries covered: United States, United Kingdom, Germany, France, Italy, Spain, Brazil, China, India, Russia, Japan, Australia, Canada, Mexico, South Korea, Denmark, Ireland, Netherlands, New Zealand, South Africa, Sweden, Switzerland, Austria, Belgium, Finland, Israel, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Taiwan, Czech Republic, Greece, Hungary, Turkey, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, Argentina and Chile.
Scope
This Market Model gives important, expert insight you won’t find in any other source. The model illustrates qualitative and quantitative trends within the specified market. This model is required reading for – – CMO executives who must have deep understanding of the Hemostasis tests market place to make strategic planning and investment decisions. – Sourcing and procurement executives who must understand crucial components of the supply base in order to make decisions about supplier selection and management. – Private equity investors that need a deeper understanding of the market to identify and value potential investment targets.
Reasons to Buy
The model will enable you to – – Understand the impact of COVID-19 on Hemostasis tests market. – Develop and design your in-licensing and out-licensing strategies through a review of pipeline products and technologies, and by identifying the companies with the most robust pipeline. – Develop business strategies by understanding the trends shaping and driving Hemostasis tests market. – Drive revenues by understanding the key trends, innovative products and technologies, market segments, and companies likely to impact the Hemostasis tests market in the future. – Formulate effective sales and marketing strategies by understanding the competitive landscape and by analyzing the company share of market leaders. – Identify emerging players with potentially strong product portfolios and create effective counter-strategies to gain a competitive advantage. – Track device sales in the global and country-specific Hemostasis tests market from 2015-2030. – Organize your sales and marketing efforts by identifying the market categories and segments that present maximum opportunities for consolidations, investments and strategic partnerships.
0 notes
Text
Othilia My SC
New Post has been published on https://nerret.com/netmyname/othilia-my/othilia-my-sc/
Othilia My SC
Othilia My SC Top Web Results.
my.sc.edu my.sc.edu Checklist for New Freshmen (Columbia Only) · Pay enrollment deposit/fee · View housing information · View orientation information · Access South Carolina …
mydorway.dor.sc.gov MyDORWAY Forgot your password? Validation. Payments. Make a Payment. Individuals. Where's My Refund? Identity Verification Quiz. Individual Code Verification …
my.sc.edu VIP ID Password Management Using your VIP ID and Password to Access Self Service Carolina … To locate your Network Username or set your password, visit my.sc.edu and sign in using …
www.sc.edu University of South Carolina The University of South Carolina is home to more than 200 years of history and tradition, rising from a single building in 1805 on what would become the heart of …
sc.edu Student Gateway | University of South Carolina Check your grades, find out how to get involved and catch the latest university … The Student Gateway connects you to everything you need across sc.edu.
my.carolinacard.sc.edu UofSC Central Authentication Service (CAS) It is the first portion of your official university email address (@mailbox.sc.edu or @email.sc.edu). Enrolled students, faculty, staff, and affiliates will use this official …
journals.sagepub.com Relationship Between Patients' Warfarin Knowledge and … From January to March 1999, 122 patients attending the warfarin clinic of the Prince of Wales Hospital in Hong Kong were interviewed. Their knowledge of …
www.urbandictionary.com Urban Dictionary: sc Get a sc mug for your fish Trump. … Sc stands for Snap Chat, a Social Media where you can take pictures or film 10 second videos with filters including dog faces …
us.battle.net Technical Support – StarCraft II Forums My Account. %USER_BATTLETAG_FULL%. Blizzard. Overwatch™. World of … %PROMO_TEXT%. %PROMO_LINK_TEXT% · StarCraft II · Forums Technical …
www.teamliquid.net StarCraft 2 Live Stream List 18 Classic BW VODs 24/7 Classic Starcraft VoD stream 2000-2012 (6344 VoDs) Preview 6 NightEnD NightEnD Northrend Ladder Preview 0 OGamingTV SC2 …
0 notes
Text
Latest Updates on CPT Code for INR Test in 2024
The CPT code for INR test is a vital component in medical billing, ensuring accurate documentation and seamless reimbursement for coagulation testing. In 2024, several updates have been introduced to simplify processes, improve accuracy, and comply with regulatory changes. Whether you're a healthcare provider, medical coder, or patient, understanding these updates is crucial for efficient healthcare management.
What Is the CPT Code for INR Test?
The CPT code for INR test refers to the procedural terminology used in medical billing to identify and document an International Normalized Ratio (INR) test. This test evaluates blood clotting and is crucial for patients on anticoagulant therapy, such as warfarin. Correct use of this CPT code ensures proper billing and reimbursement, making it an integral part of healthcare operations.
Why Are Updates to the CPT Code for INR Test Important?
Each year, the American Medical Association (AMA) reviews and updates the CPT codes to reflect advancements in medical technology, changes in clinical practices, and regulatory requirements. Updates to the CPT code for INR test in 2024 aim to:
Enhance clarity in documentation.
Address gaps in coding practices.
Align with modern testing methods and equipment.
Key Updates to the CPT Code for INR Test in 2024
. Addition of New Testing Scenarios
The CPT code for INR test now includes provisions for newer point-of-care testing methods. These updates allow providers to use the same code for traditional lab-based tests and modern INR monitoring devices, ensuring flexibility and comprehensive documentation.
. Improved Descriptions for Accuracy
To reduce ambiguities, the descriptions associated with the CPT code for INR test have been refined. This change makes it easier for coders and billers to select the correct code, avoiding errors that could lead to claim denials or delayed reimbursements.
. Updates for Telehealth Services
With the growing adoption of telehealth, the 2024 revisions include guidelines on using the CPT code for INR test for remote INR monitoring. This ensures that healthcare providers offering virtual care can document and bill accurately.
. Enhanced Compliance Standards
The new updates emphasize compliance with Medicare and Medicaid regulations. Using the CPT code for INR test correctly now requires adherence to stricter documentation practices, ensuring transparent and audit-proof claims.
How to Stay Updated on CPT Code Changes
Regular Training and Certifications
Healthcare professionals should participate in regular training to stay informed about updates to the CPT code for INR test. This ensures accurate coding and minimizes errors in billing.
Access Reliable Resources
Subscribe to trusted sources like the AMA or healthcare industry journals for the latest news on CPT code revisions. Tools like coding manuals and online databases can provide detailed insights into the 2024 changes.
Partner with Experts
Working with certified medical coders or outsourcing billing operations to experienced professionals can ensure that the CPT code for INR test is applied correctly.
Benefits of Staying Updated
Adopting the latest practices for the CPT code for INR test offers several advantages:
Improved Accuracy: Reduces errors in claim submissions.
Faster Reimbursement: Ensures timely payments from insurance providers.
Compliance Assurance: Meets regulatory requirements effectively.
Streamlined Operations: Enhances efficiency in medical billing processes.
The 2024 updates to the CPT code for INR test reflect the evolving needs of the healthcare industry, prioritizing accuracy, flexibility, and compliance. Staying informed about these changes is essential for healthcare providers, coders, and patients to ensure seamless billing and quality care. By adopting the latest practices, you can enhance operational efficiency and avoid potential challenges.
For expert insights and reliable solutions, trust PatientSelfTesting to guide you through the nuances of the CPT code for INR test and ensure a smooth medical billing experience.
0 notes
Text
How to Verify Your PT/INR Medicare Coverage Before Your Test
For individuals who are on blood-thinning medications like warfarin, regularly testing their Prothrombin Time and International Normalized Ratio (PT/INR) is essential to managing their health. Since these tests are often performed regularly, it’s important to ensure that they are covered by Medicare to avoid unexpected costs. In this blog, we’ll guide you through the steps on how to verify your PT/INR Medicare coverage before your test, ensuring peace of mind and financial readiness.
Understanding PT/INR Testing and Medicare Coverage
Before diving into the steps to verify your coverage, it’s essential to understand what PT/INR testing is and how Medicare plays a role. PT/INR tests measure how long it takes for your blood to clot and help monitor the effectiveness of blood-thinning medications like warfarin. Medicare Part B typically covers PT/INR testing for those who require it due to their medical condition or medications, but coverage details can vary.
Steps to Verify Your PT/INR Medicare Coverage
Verifying your PT/INR Medicare coverage doesn’t have to be complicated. By following these steps, you can ensure that your test is covered before you head to the lab or your healthcare provider.
. Confirm Medicare Eligibility for PT/INR Coverage
The first step is to ensure that you are eligible for Medicare coverage of PT/INR tests. Medicare Part B covers these tests for individuals who are prescribed warfarin or other anticoagulant medications. However, there are certain requirements that need to be met:
Your healthcare provider must deem the test medically necessary.
The test must be conducted in a Medicare-approved laboratory.
You need a physician’s referral or prescription for the test.
. Check with Your Medicare Plan Provider
It’s crucial to check the specifics of your Medicare plan. If you are enrolled in a Medicare Advantage Plan (Part C), coverage may vary compared to Original Medicare (Part A and Part B). Here’s how you can do that:
Call your Medicare plan provider directly and inquire about coverage details for PT/INR testing.
Ask for specific information on any copayments, deductibles, or coverage limits that may apply.
Verify whether your preferred healthcare provider or testing center is within your Medicare network.
. Speak with Your Healthcare Provider
Your healthcare provider plays a key role in ensuring that your PT/INR test is covered by Medicare. Speak with your doctor or specialist to confirm the following:
They have submitted the necessary documentation and referrals to Medicare.
The test is scheduled at a Medicare-approved facility or laboratory.
They have coded the test correctly to reflect that it is medically necessary, which can affect your coverage.
. Review Your Medicare Summary Notice (MSN)
After your PT/INR test, Medicare will send you a Medicare Summary Notice (MSN) that details the services and tests covered. Review this document carefully to ensure that your PT/INR test is listed as covered and that you understand any associated costs. If the test is not covered or there is a discrepancy, contact Medicare or your healthcare provider to resolve the issue.
. Use Medicare’s Online Tools
Medicare offers online tools that can help you verify coverage before your PT/INR test. You can visit the official Medicare website to:
Search for PT/INR test coverage using their “What’s Covered” tool.
Review specific coverage rules for different plans and testing requirements.
Find information on Medicare-approved providers and laboratories near you.
What to Do If Your PT/INR Test Isn’t Covered
If, after verifying your PT/INR Medicare coverage, you find that your test isn’t covered, don’t panic. There are steps you can take to minimize out-of-pocket costs:
Appeal the decision: If Medicare denies coverage for your test, you have the right to file an appeal. Work with your healthcare provider to provide additional documentation supporting the medical necessity of the test.
Look for financial assistance programs: Many healthcare providers and organizations offer financial assistance programs for individuals who need regular PT/INR testing but cannot afford the costs.
Consider alternative testing options: Home PT/INR testing kits are becoming more widely available and may be covered by Medicare if prescribed by a healthcare provider.
Verifying your PT/INR Medicare coverage before your test is essential to avoid unexpected costs and ensure that you receive the care you need. By confirming eligibility, speaking with your Medicare provider and healthcare professional, and reviewing your Medicare Summary Notice, you can feel confident that your PT/INR test is covered.
At PatientSelfTesting, we understand how critical PT/INR testing is to your health and well-being. That’s why we encourage you to take the necessary steps to verify your PT/INR Medicare coverage before your test. By doing so, you’ll have peace of mind and focus on what matters most—your health.
0 notes
Text
How the PT/INR Labcorp Code Can Help Prevent Complications
In the realm of healthcare, precise diagnostics and timely interventions are paramount in preventing complications and ensuring optimal patient outcomes. One such critical diagnostic tool is the PT/INR test. For patients on anticoagulant therapy, maintaining the right balance is crucial to avoid both bleeding complications and thrombotic events. This blog explores how the PT/INR Labcorp Code can help prevent complications, ensuring that patients receive the best possible care.
Understanding PT/INR Testing
Prothrombin Time (PT) and International Normalized Ratio (INR) tests are essential for monitoring blood clotting tendencies. The PT test measures how long it takes for blood to clot, while the INR standardizes these results regardless of the testing method. For patients on anticoagulants like warfarin, regular PT/INR testing is necessary to ensure that their blood clotting time remains within a therapeutic range.
The Importance of the PT/INR Labcorp Code
Labcorp, a leading global life sciences company, provides a specific code for PT/INR testing. The PT/INR Labcorp Code simplifies the process for healthcare providers to order and interpret these crucial tests. Here’s how the PT/INR Labcorp Code can help prevent complications:
. Streamlined Test Ordering
The PT/INR Labcorp Code streamlines the ordering process for healthcare providers. By using this specific code, providers can ensure that the correct test is ordered every time, reducing the risk of errors. Accurate test ordering is the first step in preventing complications, as it ensures that patients receive the appropriate monitoring for their anticoagulant therapy.
. Standardized Results
One of the key benefits of using the PT/INR Labcorp Code is the standardization of results. The INR component of the test is particularly important for standardizing PT results, making it easier to compare results from different laboratories. This standardization ensures that healthcare providers can accurately assess a patient’s anticoagulation status, regardless of where the test was performed. Accurate and consistent results are crucial for adjusting medication dosages and preventing complications.
. Enhanced Patient Monitoring
Regular and accurate PT/INR testing is essential for patients on anticoagulants. The PT/INR Labcorp Code facilitates timely and consistent testing, enabling healthcare providers to monitor patients more effectively. Enhanced monitoring helps in early detection of any deviations from the therapeutic range, allowing for prompt intervention. By closely monitoring PT/INR levels, healthcare providers can prevent complications such as excessive bleeding or clot formation.
. Improved Communication Between Healthcare Providers
Using the PT/INR Labcorp Code also improves communication between different healthcare providers involved in a patient’s care. Standardized test ordering and results make it easier for primary care physicians, specialists, and other healthcare professionals to share and interpret information. Improved communication ensures that all members of the healthcare team are on the same page, providing cohesive and coordinated care to prevent complications.
. Facilitating Patient Self-Testing
For some patients, self-testing their PT/INR levels at home can be a convenient and effective way to manage their anticoagulation therapy. The PT/INR Labcorp Code can be integrated into patient self-testing programs, ensuring that self-reported results are consistent and reliable. By empowering patients to take an active role in their healthcare, self-testing can lead to better adherence to treatment plans and more timely interventions, ultimately preventing complications.
In conclusion, the PT/INR Labcorp Code is a vital tool in the management of anticoagulation therapy. By streamlining test ordering, standardizing results, enhancing patient monitoring, improving communication between healthcare providers, and facilitating patient self-testing, the PT/INR Labcorp Code can help prevent complications and ensure optimal patient outcomes.
At PatientSelfTesting, we recognize the importance of accurate and consistent PT/INR testing. Our services are designed to support both healthcare providers and patients in achieving the best possible care. By utilizing the PT/INR Labcorp Code, you can ensure that your anticoagulation therapy is closely monitored and managed, reducing the risk of complications and improving your overall health.
0 notes
Text
The Role of the INR CPT Code in LabCorp's Diagnostic Services
In the realm of diagnostic services, precision and accuracy are paramount. One essential component in ensuring such precision is the use of Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes. Among these, the INR CPT code plays a critical role, particularly in the services provided by LabCorp. This blog explores the significance of the INR CPT code in LabCorp's diagnostic services, highlighting its importance in patient care and clinical decision-making.
Understanding the INR CPT Code
The International Normalized Ratio (INR) is a standardized number that's calculated based on the results of a prothrombin time (PT) test. It is used to monitor patients who are on anticoagulant therapy, such as warfarin. The INR CPT code is a specific code used by healthcare providers to report and bill for this test. This code ensures that the test is accurately recorded, facilitating proper reimbursement and data tracking.
Ensuring Accurate Monitoring of Anticoagulant Therapy
Anticoagulant therapy is critical for patients with conditions such as atrial fibrillation, deep vein thrombosis, or pulmonary embolism. These patients require regular monitoring to ensure their blood clotting time remains within a therapeutic range, thus preventing either bleeding complications or thrombotic events. The INR CPT code enables LabCorp to provide precise and consistent monitoring, ensuring that patients receive the correct dosage adjustments and optimal care.
Facilitating Efficient Diagnostic Processes
LabCorp utilizes the INR CPT code to streamline its diagnostic processes. This code helps in standardizing the test procedure across various labs, ensuring that all tests are conducted uniformly and results are comparable. By using the INR CPT code, LabCorp can efficiently process a large number of tests, reducing turnaround times and improving overall service delivery.
Enhancing Data Accuracy and Billing
Accurate data is crucial in healthcare, not only for patient care but also for administrative purposes such as billing and reporting. The INR CPT code ensures that all tests are accurately recorded in LabCorp’s system. This precision aids in reducing billing errors and ensures that insurance claims are processed smoothly. For patients, this means fewer disputes over medical bills and a clearer understanding of their medical expenses.
Supporting Clinical Decision-Making
The role of the INR CPT code extends beyond billing and administrative functions. It is integral to clinical decision-making. Accurate INR results are critical for physicians to make informed decisions about a patient's anticoagulant therapy. LabCorp's use of the INR CPT code ensures that test results are reliable and timely, providing doctors with the necessary information to adjust treatments promptly and effectively.
Promoting Standardization and Compliance
Standardization is a key aspect of modern healthcare, ensuring that tests and treatments are consistent and reliable. The INR CPT code promotes this standardization within LabCorp's diagnostic services. By adhering to standardized coding practices, LabCorp ensures compliance with healthcare regulations and maintains high-quality testing standards. This compliance is crucial for patient safety and the credibility of diagnostic services.
The INR CPT code is a vital element in LabCorp's diagnostic services, playing a pivotal role in ensuring accurate monitoring of anticoagulant therapy, streamlining diagnostic processes, enhancing data accuracy, and supporting clinical decision-making. It promotes standardization and compliance, ensuring that patients receive reliable and high-quality care.
For those managing anticoagulant therapy, understanding the importance of the INR CPT code is crucial. By recognizing its role, patients and healthcare providers can better appreciate the value of precise and standardized diagnostic testing.
To learn more about the INR CPT code and how it impacts your health, visit patientselftesting. LabCorp’s commitment to using precise diagnostic codes like the INR CPT code ensures that you receive the best possible care, keeping your health and safety at the forefront.
0 notes
Text
Importance of Biomedical Waste Removal in Winter Garden and Alafaya, FL
Throwing unused drugs and remnants of medicines in ordinary trash is a strict no-no. It is essential to check the regulations made public by the Federal Government and the State to learn about compliance. Proper pharmaceutical waste disposal in Winter Garden and Alafaya, FL, must be ensured to escape heavy penalties. Doctor’s offices and medical facilities also risk being closed permanently for violation of the rules.
All facilities need to abide by the rules. While the owner or management may be aware of the must-dos, they are responsible for educating, training, and providing the necessary documentation to their workers. It is essential for all concerned to know the following facts:-
What Pharmaceuticals Must Be Discarded?
Well, pharmaceutical wastes are usually expired or used prescription drugs. It may also refer to personal care products used at home. The following are generally included in the list:
All P-Listed Waste Found Under The Code Of Federal Regulations (CFR) Title 40, Part 261.30 (Subpart D) Listed As Hazardous Wastes
· Cytotoxic Medications Used For Chemotherapy Treatments
· Fluorouracil Creams Used For Cancer Treatment
· Anti-Viral Agents
· Anesthetic Agents
· Hormone Creams Or Pills
· Warfarin Or Related Medicines
Such drugs or remnants of these medications are labeled as hazardous because of certain factors. These may be toxic or have the potential to injure tissues and even cause damage to major organs. They need to be stored carefully and disposed of according to the regulations.
What is strictly forbidden?
The regulations have been altered over the years, along with scientific breakthroughs. Apart from forbidding faulty disposal methods, the present-day stipulations also aim to preserve the environment. The following practices are frowned upon, with the offender being penalized heavily:-
· Dumping expired pharmaceutical compounds in the drain
· Throwing the medicines, both expired and usable, into the ordinary garbage bag
· Using any other container for storage apart from the color-coded container recommended by OSHA violates safety practices. One must thus source the red-colored container to store the pharmaceuticals until the company collects them hired to do so.
Guidance for proper disposal of pharmaceutical waste
It is most important to connect with a licensed waste management facility instead of trying to do it at the facility. Such an action may result in inadvertent errors and spread contamination among the staff, patients, and visitors of the medical facility/research laboratory.
· Identification of pharmaceutical waste by going through the list of medicines sourced from multiple pharmacies/ companies/ manufacturers
· Segregation is another essential part of the process. The unused drugs the patient or the staff had not opened may be returned to the manufacturer. The strips containing a few tablets/capsules should go into the red storage bag. Likewise, storing the chemotherapy or cancer-related drugs must be done correctly to prevent cross-contamination.
· Finally, the waste management facility will transport and dispose of the waste as per the norms.
All facilities, laboratories, and diagnostic centers are advised to adhere to the regulations for biomedical waste removal in Winter Garden and Alafaya, FL.
#pharmaceutical waste disposal in Winter Garden and Alafaya#FL#biomedical waste removal in Winter Garden and Alafaya
0 notes
Text
Understanding PT/INR LabCorp Test Code: A Comprehensive Guide
In the realm of healthcare, understanding medical tests and their associated codes is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers. One such test that plays a vital role in monitoring blood clotting levels is the PT/INR LabCorp Test Code. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into what exactly this test entails, its significance in healthcare, and how it can benefit patients and medical professionals alike.
What is PT/INR LabCorp Test Code?
The PT/INR LabCorp Test Code refers to the laboratory code used by LabCorp, one of the leading providers of clinical laboratory services, to identify and process tests related to Prothrombin Time (PT) and International Normalized Ratio (INR). PT/INR testing is essential for assessing the clotting ability of blood and monitoring patients on anticoagulant therapy, such as warfarin.
Understanding Prothrombin Time (PT) and International Normalized Ratio (INR):
Prothrombin Time (PT) measures the time it takes for blood to clot. It is often used to monitor the effectiveness of anticoagulant medications and to diagnose bleeding disorders. International Normalized Ratio (INR) is a standardized method of expressing PT results, ensuring consistency across different laboratories and testing methods. A higher INR value indicates a longer clotting time, while a lower value suggests a faster clotting time.
Importance in Healthcare:
The PT/INR LabCorp Test Code holds immense importance in healthcare for several reasons:
. Monitoring Anticoagulant Therapy: Patients on anticoagulant therapy require regular PT/INR testing to ensure their blood clotting levels remain within a therapeutic range. This helps prevent both clotting disorders and excessive bleeding.
. Diagnosis and Management of Clotting Disorders: PT/INR testing is instrumental in diagnosing and managing various clotting disorders, such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary embolism (PE), and atrial fibrillation.
. Precision Medicine: By accurately monitoring PT/INR levels, healthcare providers can tailor anticoagulant therapy to each patient's individual needs, optimizing treatment outcomes and reducing the risk of complications.
How PT/INR LabCorp Test Code Works:
When a healthcare provider orders a PT/INR test using the LabCorp Test Code, a blood sample is collected from the patient and sent to a LabCorp facility for analysis. The laboratory then performs the PT and INR assays using standardized protocols and equipment. Once the results are available, they are reported back to the ordering physician for interpretation and further action.
Benefits for Patients:
Patients stand to benefit greatly from PT/INR LabCorp testing:
. Peace of Mind: Regular PT/INR testing provides patients with peace of mind, knowing that their anticoagulant therapy is effectively managed and their clotting levels are within a safe range.
. Reduced Risk of Complications: By closely monitoring PT/INR levels, patients can reduce their risk of both clotting events and bleeding complications associated with anticoagulant therapy.
. Empowerment through Knowledge: Understanding their PT/INR results empowers patients to actively participate in their healthcare decisions and adhere to their treatment plans more effectively.
Benefits for Healthcare Providers:
Healthcare providers also benefit from the PT/INR LabCorp Test Code:
. Enhanced Patient Care: PT/INR testing enables healthcare providers to deliver personalized care to patients, optimizing treatment strategies based on individual PT/INR profiles.
. Streamlined Monitoring: With access to standardized PT/INR testing through LabCorp, healthcare providers can streamline the monitoring process and ensure consistency in results interpretation.
. Improved Patient Outcomes: By effectively managing PT/INR levels, healthcare providers can improve patient outcomes, reducing the incidence of clotting events, bleeding complications, and hospital readmissions.
In conclusion, understanding the PT/INR LabCorp Test Code is essential for patients and healthcare providers alike. By leveraging this comprehensive guide, patients can gain insight into the significance of PT/INR testing and its impact on their health and well-being. Likewise, healthcare providers can utilize the PT/INR LabCorp Test Code to enhance patient care, improve treatment outcomes, and promote overall wellness. For more information on PT/INR testing and patient self-testing options, visit PatientSelfTesting and discover the benefits of proactive PT/INR management firsthand.
0 notes
Text
Improving Patient Outcomes: The Impact of Accurate CPT Code for PT INR
In the dynamic landscape of healthcare, the accurate reporting and documentation of medical procedures are vital components that directly impact patient care and reimbursement processes. One such critical element in the realm of hematology and coagulation testing is the CPT Code for PT INR, playing a pivotal role in monitoring anticoagulation therapy. In this blog post, we will delve into the significance of assigning and documenting the accurate CPT Code for PT INR and its profound impact on improving patient outcomes.
Understanding the Basics of CPT Code for PT INR
The Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) Code for PT INR refers to the specific code assigned to the Prothrombin Time (PT) International Normalized Ratio (INR) test. This test is commonly used to monitor patients on anticoagulation therapy, such as those taking Warfarin. Accurate coding is essential for proper billing, reimbursement, and overall healthcare management.
The Link Between Accurate Coding and Patient Care
Accurate CPT coding for PT INR is directly correlated with patient care outcomes. When healthcare providers assign the correct code, it ensures that the patient's anticoagulation levels are precisely monitored. This, in turn, contributes to better management of clotting disorders, reducing the risk of thrombosis or bleeding complications.
Impact on Reimbursement Processes
In the intricate web of healthcare, proper reimbursement is crucial for sustaining medical practices and ensuring quality patient care. Accurate CPT coding for PT INR facilitates smooth reimbursement processes, preventing claim denials and delays. Healthcare providers who consistently use the correct CPT Code for PT INR contribute to efficient billing cycles, allowing them to focus on patient care rather than navigating financial hurdles.
Common Errors and How to Avoid Them
Despite its importance, assigning the CPT Code for PT INR accurately can be challenging. Common errors include code mismatch, lack of documentation, and outdated coding practices. To mitigate these issues, healthcare professionals should stay informed about the latest coding guidelines, engage in ongoing training, and utilize coding resources provided by reputable organizations.
Strategies for Improving Coding Accuracy
To enhance coding accuracy for PT INR, healthcare facilities can implement a combination of technology and training. Utilizing electronic health record (EHR) systems with integrated coding support can reduce errors and streamline the coding process. Additionally, ongoing training programs for medical coders ensure that they stay updated on coding guidelines and best practices.
The Role of Patient Education
Patients are integral partners in the healthcare journey, and educating them about the importance of accurate CPT coding for PT INR is paramount. Patient understanding can lead to improved compliance with testing regimens, better communication with healthcare providers, and ultimately, enhanced outcomes.
PatientSelfTesting: Leading the Way in Accurate CPT Coding for PT INR
As a pioneering force in patient-centric healthcare, PatientSelfTesting recognizes the critical role that accurate CPT coding plays in improving patient outcomes. By advocating for precision in coding, PatientSelfTesting empowers healthcare providers and patients alike to navigate the complexities of anticoagulation therapy with confidence.
In conclusion, accurate CPT coding for PT INR is not just a procedural formality but a cornerstone in the edifice of quality healthcare. From its impact on patient care to its role in reimbursement processes, the importance of getting it right cannot be overstated. By embracing accurate coding practices, healthcare providers contribute significantly to improving patient outcomes and ensuring the overall well-being of those under their care.
0 notes